Introduction
Frozen shoulder, also known as adhesive capsulitis, is a condition characterized by pain and stiffness in the shoulder joint. It typically progresses through three stages: freezing, frozen, and thawing, each lasting several months. The condition can significantly impact daily activities, making physiotherapy a crucial component of management.
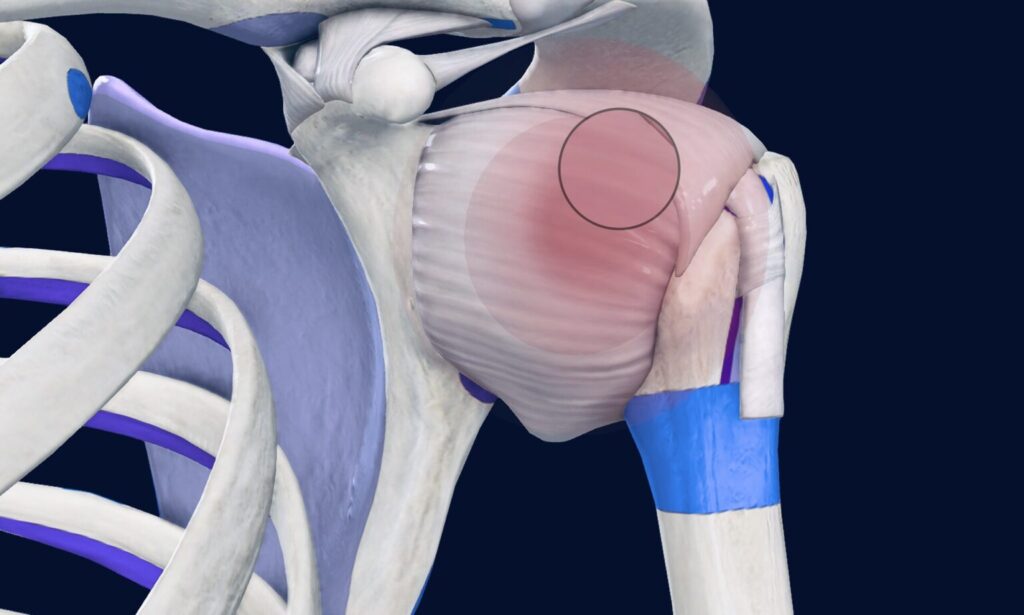
Key Pathophysiological Mechanisms
- Inflammatory Response
- Early immune activation leads to elevated cytokines, particularly transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β1), which stimulates fibroblast proliferation.
- Increased alarmins and binding to receptors for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) contribute to inflammation.
- Fibrosis and Capsular Thickening
- Fibroblasts differentiate into myofibroblasts, producing excessive Type III collagen, causing capsular thickening and stiffness.
- The coracohumeral ligament and rotator interval are particularly affected, leading to mechanical restriction.
- Vascular and Neural Changes
- Reduced microcirculation within the capsule exacerbates fibrosis.
- Neural involvement leads to pain hypersensitivity, contributing to discomfort during movement.

Stages of Frozen Shoulder
- Freezing Stage (Inflammatory phase) – Pain and progressive stiffness.
- Frozen Stage (Fibrotic phase) – Severe restriction of movement.
- Thawing Stage (Recovery phase) – Gradual improvement in mobility.
Causes and Risk Factors
Frozen shoulder often develops due to:
- Prolonged immobilization (e.g., post-surgery or injury)
- Diabetes (higher prevalence among diabetics)
- Thyroid disorders
- Autoimmune conditions
- Age and gender (more common in individuals aged 40–60, especially women)
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms
- Gradual onset of pain and restricted movement
- Difficulty in performing overhead activities
- Night pain affecting sleep
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination assessing range of motion
- Imaging tests (X-ray, MRI) to rule out other conditions
Best Physiotherapy Management
Physiotherapy plays a vital role in reducing pain, improving mobility, and restoring function. The following techniques are commonly used:
1. Pain Management
- Heat and cold therapy to reduce inflammation
- Electrotherapy (TENS, ultrasound) for pain relief
- Manual therapy (soft tissue mobilization)
2. Mobility Restoration
- Passive range of motion (PROM) exercises
- Active-assisted range of motion (AAROM) exercises
- Stretching techniques (pendulum exercises, towel stretches)
3. Strengthening Exercises
- Isometric exercises for shoulder stability
- Rotator cuff strengthening
- Resistance band exercises
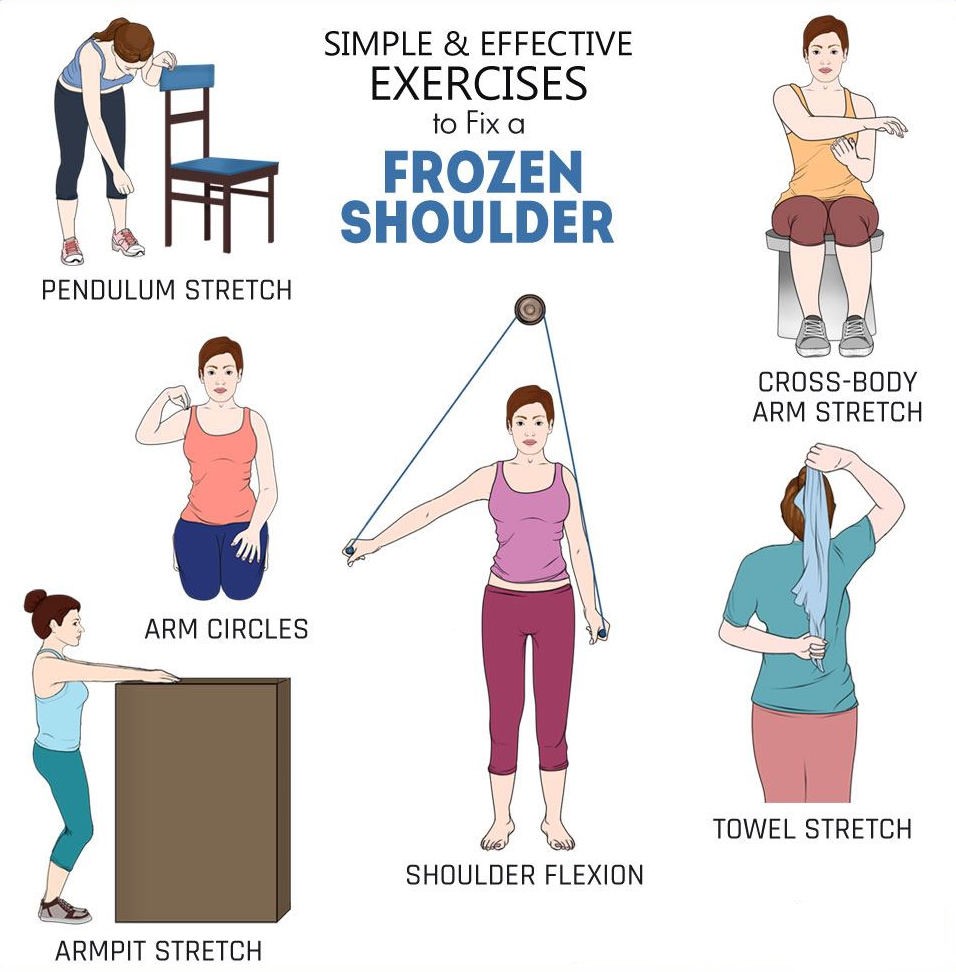
Recent advancements in physiotherapy for frozen shoulder focus on improving mobility, reducing pain, and enhancing shoulder function. Here are some promising techniques:
- Matrix Rhythm Therapy – Helps improve tissue elasticity and circulation, reducing stiffness and pain.
- Movement with Mobilization (MWM) – A manual therapy technique that enhances joint mobility and function.
- Sleeper’s Stretch – A targeted stretch to improve internal rotation and flexibility.
- Gong’s Mobilization – A specialized mobilization technique showing positive outcomes in pain relief and range of motion.
- Combination Therapy – Integrating suprascapular nerve block (SSNB), intra-articular corticosteroid (IACS) injections, hydrodilatation, and physiotherapy for better result
- Hydrotherapy
- Water-based exercises provide pain-free movement, enhancing recovery.
- Shockwave Therapy
- Used for pain relief and tissue regeneration, showing promising results in frozen shoulder management.
- Preventive Measures
- Regular shoulder mobility exercises
- Posture correction
- Avoiding prolonged immobilization
The prognosis of physiotherapy treatment depends on various factors, including the condition being treated, patient adherence, and individual health status. Here are some key insights:
- Musculoskeletal Pain Recovery – Studies show that only half of patients report satisfactory symptom relief after six months of physiotherapy.
- Clinician Predictions Matter – Experienced physiotherapists can often predict which patients will have better recovery outcomes, with prognosis influencing disability improvement and recovery rate.
- Patient Expectations Play a Role – Research suggests that patients with positive recovery expectations tend to have better functional outcomes in musculoskeletal physiotherapy
Here are some research papers on Physiotherapy Management for Frozen Shoulder that provide evidence-based insights:
- Evaluate the effectiveness of Physiotherapy
management in the Frozen Shoulder: A Case study
1Saidu Salisu Jawa, BPT, Lovely Professional University
1Prabhjot Kaur, BPT, Lovely Professional University,
2Dr. Sakshi Sadhu, Assistant Professor, Lovely Professional University Phagwara, Punjab.
2. Review on Physiotherapy Management on Frozen
Shoulder
Diksha Nagrale1, Pankhuri Multani1, Anagha Armarkar1, Pooja Wade2,
Leena Jaiswal3
1Professor, Smt. Radhikatai Pandav College of Physiotherapy, Nandanvan, Nagpur, India
2Associate Professor, Smt. Radhikatai Pandav College of Physiotherapy, Nandanvan, Nagpur, India.
3Assistant Professor, Smt. Radhikatai Pandav College of Physiotherapy, Nandanvan, Nagpur, India.
3. The Efficacy of Manual Therapy Techniques in the
Management of Frozen Shoulder: A Systematic
Review and Meta-analysis
*Dr.Pooja Katiyar (Physiotherapist), Assistant Professor
*Ms. Shikha Kumari ( Assistant professor)
For Best Physiotherapy Treatment and More Educational Content login to
Recovery Physiotherapy Centre
C/646, Koelnagar
Rourkela,Odisha,India
Contact – 9556135581
